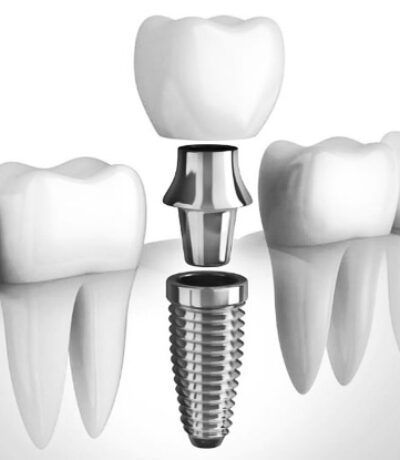
What are dental implants?
Dental implants are titanium or ceramic posts or frames surgically inserted into the jawbone beneath your gums. They are an artificial replacement for the tooth root and enable your dentist to mount replacement teeth. Replacement can be made of ceramic or a metal and ceramic combination.
Smart surfaces of dental implants help better connectivity with the bone and fight off infection, reducing the possibility of implant rejecting. Surface layer melts in time, releasing calcium and phosphate which encourage bone growth. Bone grows into the implant surface, which makes the implant more functional by taking over a part of pressure from the bone when chewing. Silver nanoparticles are included into the surface layer to reduce infection. With melting, silver with antimicrobial action is released. This way, the quantity of antibiotics is limited and protection is secured at the place of the implant to fight off infection.
There is a whole range of implants on the market, but only premium types are equipped with these properties.
Who is a candidate for dental implants?
Dental implants carry a range of risks. There are ways, of course, to decrease these risks. Choice of adequate therapy for each individual patient will depend on understanding these aspects, good and opened communication between the patient and the doctor, risk assessment and will and possibilities to reduce the mentioned risks. If all the possible topics were opened and discussed, long-term satisfaction of the patient is guaranteed. It’s best to keep a written form of this, so the patient would have a reminder of maintenance recommendations and habits. This approach reduces undesirable situations to a minimum.
Implant placement
Procedure is identical for one or multiple implants.
Sequence of teeth implants placement is as follows: analysis of the 3D orthopanomography image gives data necessary for working out a therapy plan – depending on the quantity of jawbone present for the dental implant insertion. After the plan had been made and medical treatment in preparation for the intervention prescribed, the intervention can begin. Length of the intervention ranges from half an hour for a single implant to several hours for multiple implants. Patient comes for checkup the following day, after which we wait for three or four months for bones and implant to grow together.
Temporary replacement defines shape and color of resulting teeth so the patient has a chance to get a reliable impression about the new teeth and discuss this with the doctor. We do this to secure patient satisfaction. This is mostly about color, shape and size of the teeth.
It takes 7 to 14 days to fabricate final crowns or dentures. At our office, we prefer crowns fixated with screws to those secured with dental cement, because they give us the opportunity to take them out and adjust if need be in the future. This isn’t a possibility with cemented crowns.
Sinus lift
Most common obstacle for implantation is the lack of bone due to a natural cavity in the maxillary sinus. Sinus lift is an operation of adding a bone graft in the upper jaw, in the area of premolar and molar teeth. Bone is added between the jaw bone and maxillary sinuses, which are placed on both sides of the nose. Intervention is performed by an oral or maxillofacial surgeon and after it, the implantation continues. If the patient would like to avoid additional interventions like sinus lift, alternative options are suggested, like implant retained dentures, where implants are placed in zones with enough bone.
Sedation is an option with demanding interventions or exceptionally frightened patients. All interventions can be performed with sedation, especially more complex ones, so the stress induced by the duration of surgical interventions is significantly reduced.
Computer guided implantation
No pain, no swelling, no sutures. Precise and fast implant placement is possible with a navigational model precisely determining the position of implants, defined by the processing of a 3D computer image.
Modern complete denture replacement
Situation in which the patient has no teeth left in one or both jaws is solved with a fixed prosthetic replacement or with a denture fixed on dental implants.
Fixed dentures are more comfortable for the patient because they have a natural feel. Implant retained denture is more similar to partial dentures with precise connective elements, which also guarantee stability. Difference is that with partial dentures, removable part needs to be taken out and hand washed.
Superb esthetic results are possible to achieve in both cases. Fixed dentures require six to eight implants per jaw. With implant retained dentures it is possible to place a smaller number of implants, which means a lower cost. Best case scenario, this type of denture will require four implants.
Final result is fabricated several months after placement of implants. In the meantime a temporary retainer is worn. If the patient decides to have more implants and cross over into a fixed denture, this plan is possible and should be considered in advance.